
You cannot rename one field with multiple names. If you want to rename fields with similar names, you can use a wildcard character. The rename command is used to rename one or more fields and is useful for giving fields more meaningful names, such as Process ID instead of pid. These commands are used to reformat the search results and order them based on the field values. Index=test sourcetype=access* | eval kilobytes=round(bytes/1024,2) The eval command evaluates mathematical, string, and boolean expressions.Ĭonvert the response size from bytes into kilobytes (tutorials data (sourcetype=access*) consisting of web server logs that contain a field named bytes, which represents the response size). If the field name you specify matches a field name that already exists in the search results, then the results of the eval expression overwrite the values for that field. If the field name that you specify does not match a field in the output, then a new field is added to the search results. The eval command calculates an expression and puts the resulting value into a search results field. The eval command is used to add new fields in the event by using existing fields from the event and arbitrary expressions. Search the events with failed HTTP response (HTTP response status can be found with field name status). You can only specify a wildcard (% sign) with the where command by using the “like” function. Index=test | where like(productId, “WC-SH-A%”) This search looks for events where the field foo contains the string value bar.įind the events with ProductID starts with the value WC-SH-A. This search looks for events where the field foo is equal to the field bar. Use the where command when comparing two different fields, as this cannot be done by using the search command. If the string is not quoted it is treated as a field name. Also, both commands interpret quoted strings as literals. The where command uses the same expression syntax as the eval command.

The search keeps only the results for which the evaluation was successful (that is, the Boolean result = true). The where command performs arbitrary filtering on the data and uses eval expressions to filter search results. Index=test | dedup useragent | table useragent Remove duplicate search results with the same host value. Events returned by dedup are based on search order. With dedup, you can specify the number of duplicate events to keep for each value of a single field or for each combination of values among several fields. The dedup command removes the events that contain an identical combination of values for the fields that you specify. Quotes are optional for search command, but you must put quotes when the values contain spaces.
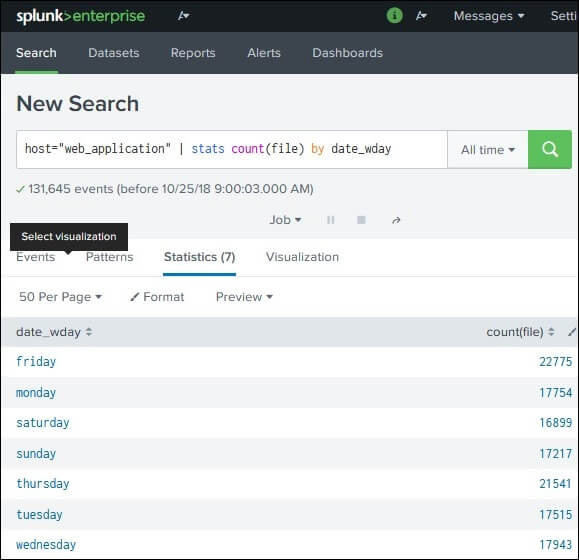
You do not need to specify the search command at the beginning of your search criteria. The search command is implied at the beginning of any search. You can retrieve events from your indexes by using keywords, quoted phrases, wildcards and key/value expressions. The search command is used to retrieve events from indexes or to filter the results of a previous search command in the pipeline.
#Splunk subsearch tutorials windows#
If you have Splunk running on Windows system use regular expression-based extract with regex value as \\(.*)\/.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
